上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Transfectamine 5000转染试剂
 |
货号 | 60022 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 5 mL | 价格 | 9948 | |
| Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | |||
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | |||
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
Transfectamine 5000转染试剂是美国AAT Bioquest生产的转染试剂,Transfectamine 5000转染试剂是一种功能强大且用途广泛的转染试剂,可将核酸引入真核细胞,引入动物细胞。它可以有效地将各种有效载荷转染到各种贴壁和悬浮细胞系中。它可用于质粒DNA转染以及基于siRNA和shRNA的基因敲低实验和基因表达研究。它对所有转染细胞均提供卓越的转染效率。Transfectamine 5000的低毒性也使转染细胞具有更高的生存能力。与大多数其他转染试剂相比,Transfectamine 5000更易于使用,并且不需要特殊的介质。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的Transfectamine 5000转染试剂。
产品说明书
样品实验方案
简要概述
1.准备细胞进行转染
2.准备Transfectamine 5000-DNA混合物
3.将Transfectamine 5000-DNA混合物添加到细胞培养物中
4.过夜培养
5.用适当的方法分析转染效率
溶液制备
1.工作溶液配制
1.1将2.5ug DNA与200uL无血清培养基混合。
1.2在步骤1中添加7.5 uL Transfectamine 5000。
1.3充分混合并在室温下孵育20分钟。 注意:Transfectamine 5000和DNA的比例需要针对不同的细胞系进行优化,通常:Transfectamine 5000转染试剂(uL)与DNA(ug)的比例= 3-5 uL至1ug
6孔板与10cm板样品方案
| 组成 | 6孔板(每孔) | 10厘米板 |
| 新鲜培养基 | 2ml | 6ml |
| 质粒 | ~2.5ug | 7.5-10ug |
| 无血清培养基 | 200ul | 600ul |
| Transfectamine 5000转染试剂 | 7.5ul | ~22.5ul |
样品示例及操作
1.细胞培养准备
1.1转染时将细胞培养至约90%融合。
1.2转染前用新鲜的生长培养基替换。 例如,对于6孔板,每孔用2 mL培养基替换,对于10 cm板,用6 mL培养基替换。
2.转染方案
将Transfectamine 5000 -DNA混合物添加至培养板并培养过夜。 注意:重组蛋白最早可在转染后16小时开始检测。转染后72〜96小时可观察到最大表达水平。
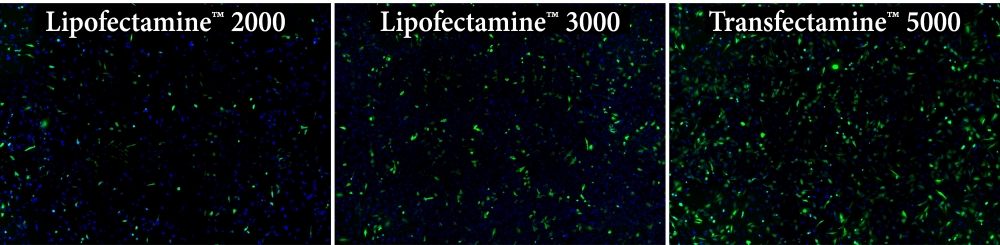
| 图1.使用Transfectamine 5000,Lipofectamine 2000和Lipofectamine 3000试剂在HeLa细胞中的转染效率比较。 每种试剂用于以96孔格式转染HeLa细胞,转染后24小时分析GFP表达。 与Lipofectamine 2000和Lipofectamine 3000试剂相比,Transfectamine 5000转染试剂可提供更高的GFP转染效率。 |
参考文献
Comparison between Lipofectamine RNAiMAX and GenMute transfection agents in two cellular models of human hepatoma
Authors: C. Berardo
Journal: Eur J Histochem (2019): ersion=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″ ?>60200.enlEndNote1117Berardo, C.Siciliano, V.Di Pasqua, L. G.Richelmi, P.Vairetti, M.Ferrigno, A.Department of Internal Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Pavia. clarissa.berardo01@universitadipavia.it.Comparison betwe
Lipofectamine 2000/siRNA complexes cause endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response in human endothelial cells
Authors: Z. Li
Journal: J Cell Physiol (2019): 21166-21181
Transfection reagent Lipofectamine triggers type I interferon signaling activation in macrophages
Authors: X. Guo
Journal: Immunol Cell Biol (2019): 92-96
Correction to: Nematollahi et al., Ternary complex of plasmid DNA with NLS-Mu-Mu protein and cationic niosome for biocompatible and efficient gene delivery: a comparative study with protamine and lipofectamine
Authors: Ternary complex of plasmid DNA with NLS-Mu-Mu protein name=”60200.enl” path=”C:UsersaatbiDropbox (AAT Bioquest)Website Working FilesProduct References60200.enl”>60200.enlEndNote4417Correction to: Nematollahi et al.
Journal: Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol (2018): 1992
Ternary complex of plasmid DNA with NLS-Mu-Mu protein and cationic niosome for biocompatible and efficient gene delivery: a comparative study with protamine and lipofectamine
Authors: M. H. Nematollahi
Journal: Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol (2018): 1781-1791
The Utilization of RNA Silencing Technology to Mitigate the Voriconazole Resistance of Aspergillus Flavus; Lipofectamine-Based Delivery
Authors: S. Nami
Journal: Adv Pharm Bull (2017): 53-59
The vector-related influences of autophagic microRNA delivery by Lipofectamine 2000 and polyethylenimine 25K on mouse embryonic fibroblast cells
Authors: C. W. Lin
Journal: Eur J Pharm Sci (2017): 11-21
Improved delivery of Cas9 protein/gRNA complexes using lipofectamine CRISPRMAX
Authors: X. Yu
Journal: Biotechnol Lett (2016): 919-29
The intracellular trafficking mechanism of Lipofectamine-based transfection reagents and its implication for gene delivery
Authors: F. Cardarelli
Journal: Sci Rep (2016): 25879
Evaluating Electroporation and Lipofectamine Approaches for Transient and Stable Transgene Expressions in Human Fibroblasts and Embryonic Stem Cells
Authors: M. Sharifi Tabar
Journal: Cell J (2015): 438-50
