上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Amplite 荧光法铅离子定量试剂盒
 |
货号 | 19007 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 200 Tests | 价格 | 3924 | |
| Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | |||
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | |||
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
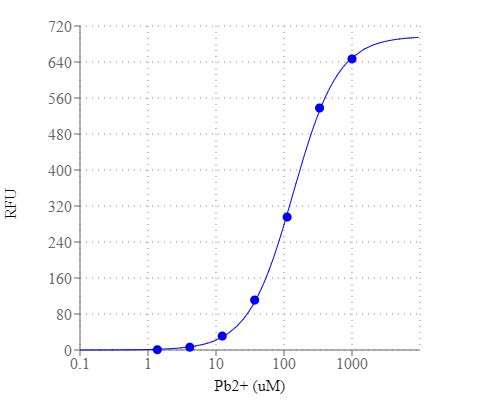
铅是一种对人类,特别是对儿童有剧毒的金属。铅干扰细胞信号和基因表达,对大脑、肝脏、肾脏会造成严重损害,甚至会导致死亡。由于其在采矿和冶炼中的悠久历史,以及在电池、油漆和汽油中的广泛应用,土壤和地下水中的铅污染一直是最严重的环境问题之一。Amplite 荧光法铅离子定量试剂盒为检测溶液中的铅离子提供了一种稳定的方法。它使用Lead Green,一种高选择性和高灵敏的绿色荧光探针,可以用荧光酶标仪(Ex/Em=490/530nm)轻松检测。Amplite 荧光法铅离子定量试剂盒可在方便的96孔或384孔微孔板中进行实验操作,且易于自动化,无需分离步骤。分析可在30分钟内完成。用Amplite 荧光法铅离子定量试剂盒,仅检测到4μM铅离子。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的Amplite 荧光法铅离子定量试剂盒。
适用仪器
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 490nm |
| 发射: | 530nm |
| cutoff: | 515nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色孔板 |
产品说明书
铅离子检测样品分析方案
概述
- 准备并添加铅标准品或测试样品(50 µL)
- 准备并添加Lead Green工作溶液(50 µL)
- 在室温下孵育10-30分钟
- 检测Ex / Em = 490/530 nm的荧光强度
溶液配制
储备溶液配制
Lead Green储备溶液(200X):将50 µL DMSO(组分D)添加到Lead Green(组分A)的小瓶中,制成Lead Green储备溶液(200X)。 注意:将未使用的Lead Green储备溶液分装在-20°C下。
标准溶液配制
将10 µL 100mM Lead标准溶液(组分C)添加到990µL H2O中以生成1mM铅标准溶液。 取1mM铅标准溶液(LS7)以H2O进行1:3连续稀释,以得到1.34至1000 µM(LS1至LS7)的系列稀释铅标准溶液。
工作溶液配制
Lead Green工作溶液:将25 µLLead Green储备溶液(200X)加入5 mL的测定缓冲液(组分B),使总体积为5.025 mL。 注意:避光,请立即使用Lead Green工作溶液,不可长时间放置。
操作步骤
表1.黑色96孔板中铅标准品和测试样品的布局。 LS =铅标准品(LS1-LS7,1.34至1000 µM); BL =空白对照; TS =测试样品。
| BL | BL | TS | TS |
| LS1 | LS1 | … | … |
| LS2 | LS2 | … | … |
| LS3 | LS3 | ||
| LS4 | LS4 | ||
| LS5 | LS5 | ||
| LS6 | LS6 | ||
| LS7 | LS7 |
表2.每个孔的试剂组成。
| Well | Volume | Reagent |
| LS1-LS7 | 50 µL | serial dilution (1.34 to 1000 µM) |
| BL | 50 µL | H2O |
| TS | 50 µL | test sample |
- 根据表1和2中提供的信息,准备铅标准品(LS),空白对照(BL)和测试样品(TS)。对于384孔板,每孔使用25 µL试剂代替50 µL。
- 在铅标准品,空白对照和测试样品的每个孔中添加50 µL Lead Green工作溶液,以使铅总测定体积为100 µL /孔。 对于384孔板,将25 µL工作溶液添加到每个孔中,而不是总体积为50 µL /孔。
- 在避光条件下,室温下孵育反应10至30分钟。
- 使用荧光酶标仪在Ex / Em = 490/530 nm处检测荧光强度。
数据分析
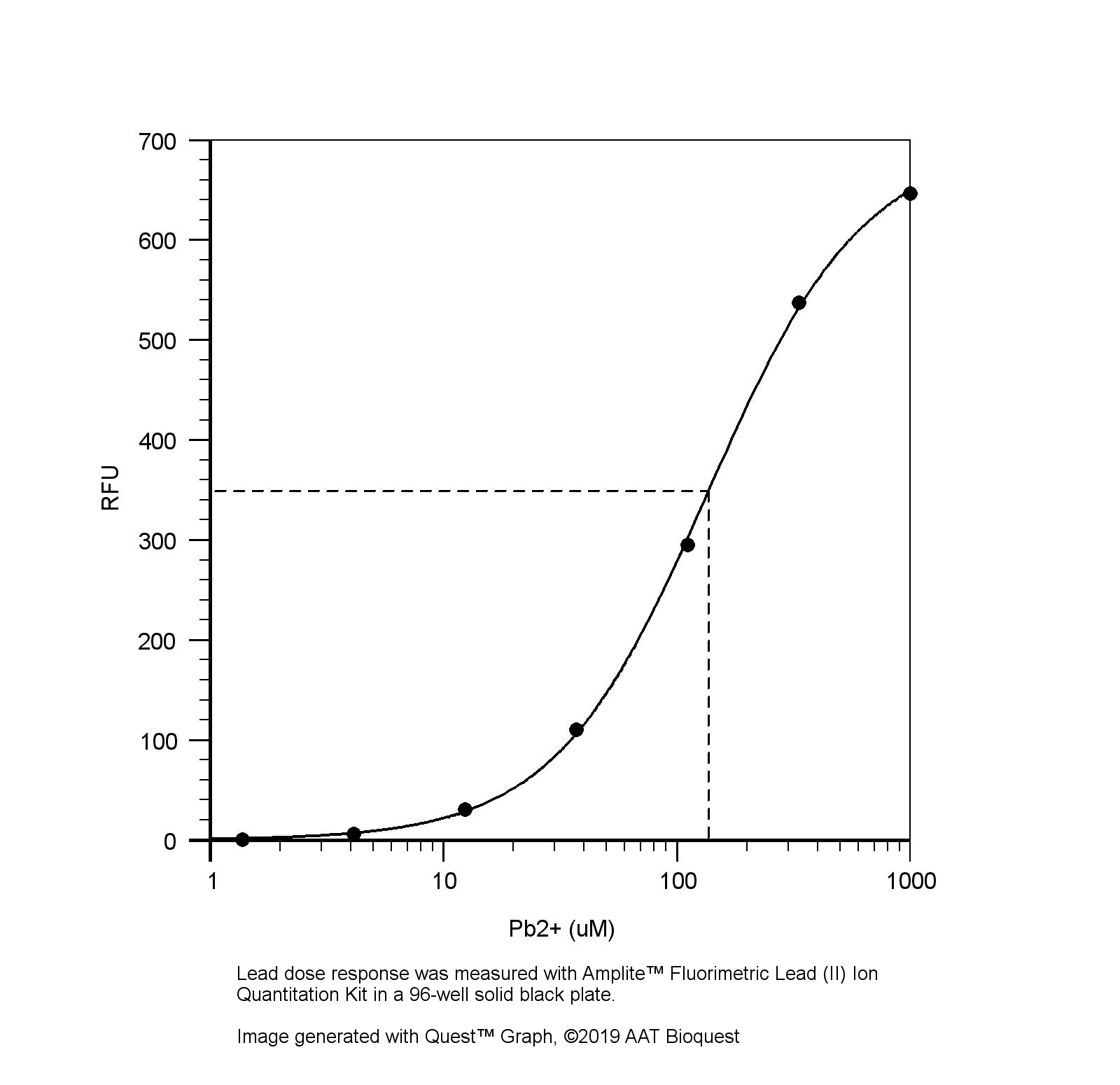
从空白标准井获得的读数(RFU)用作阴性对照。从其他标准的读数中减去该值,得到基线校正值。然后,绘制标准读数,得到标准曲线和方程。该方程可用于计算Pb2+样品。我们建议使用在线四参数物流计算器
参考文献
Lead toxicity from retained bullet fragments: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Authors: Apte, A., Bradford, K., Dente, C., Smith, R. N.
Journal: J Trauma Acute Care Surg (2019): 707-716
A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil-microbe-plant system and bioremediation strategies
Authors: Kushwaha, A., Hans, N., Kumar, S., Rani, R.
Journal: Ecotoxicol Environ Saf (2018): 1035-1045
Toxicodynamics of Lead, Cadmium, Mercury and Arsenic- induced kidney toxicity and treatment strategy: A mini review
Authors: Rana, M. N., Tangpong, J., Rahman, M. M.
Journal: Toxicol Rep (2018): 704-713
Severe Systemic Lead Toxicity Resulting From Extra-Articular Retained Shrapnel Presenting as Jaundice and Hepatitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Authors: Grasso, I. A., Blattner, M. R., Short, T., Downs, J. W.
Journal: Mil Med (2017): e1843-e1848
Retained Lumbar Bullet: A Case Report of Chronic Lead Toxicity and Review of the Literature
Authors: Bustamante, N. D., Macias-Konstantopoulos, W. L.
Journal: J Emerg Med (2016): 45-9
Systemic Lead Toxicity Secondary to Retained Intraosseous Bullet A Case Report and Review of Literature
Authors: Begly, J. P., Lajam, C. M.
Journal: Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013) (2016): 229-33
Lead toxicity in rice: effects, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies–a mini review
Authors: Ashraf, U., Kanu, A. S., Mo, Z., Hussain, S., Anjum, S. A., Khan, I., Abbas, R. N., Tang, X.
Journal: Environ Sci Pollut Res Int (2015): 18318-32
Lead toxicity: a review
Authors: Wani, A. L., Ara, A., Usmani, J. A.
Journal: Interdiscip Toxicol (2015): 55-64
A systematic review on status of lead pollution and toxicity in Iran; Guidance for preventive measures
Authors: Karrari, P., Mehrpour, O., Abdollahi, M.
Journal: Daru (2012): 2
Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates
Authors: Flora, G., Gupta, D., Tiwari, A.
Journal: Interdiscip Toxicol (2012): 47-58
